Types and uses of cotton
1. Cotton type:
Coarse cotton, also known as Asian cotton, is native to India. Due to low production and short fiber thickness, it is not suitable for machine weaving and has been eliminated.
Long staple cotton, also known as island cotton, is native to South America. Long fibers and high strength are its characteristics, suitable for spinning high count yarns. Currently, only Xinjiang produces them in China.
Fine velvet cotton - also known as upland cotton, originating from Central America, is also known as American cotton. Its characteristics include wide adaptability, high yield, long fiber length, and good quality, making it suitable for spinning medium count yarns.
2. Purpose
According to the length and appearance of fibers, cotton can be divided into three categories:
The first type of fiber is slender (within a length range of 2.5 to 6.5 centimeters) and glossy, including high-quality island cotton, Egyptian cotton, and Pima cotton; Long staple cotton has a low yield, high labor cost, and high price, mainly used for high-end fabrics, cotton yarn, and knitwear.
The second category includes generally medium length cotton (approximately 1.3 to 3.3 centimeters in length);
The third type is cotton with short and coarse fibers (approximately 1 to 2.5 centimeters in length) used to make carpets, cotton blankets, and low-cost fabrics, or blended with other fibers. Cotton is one of the most important crops in the world, with high yields and low production costs.
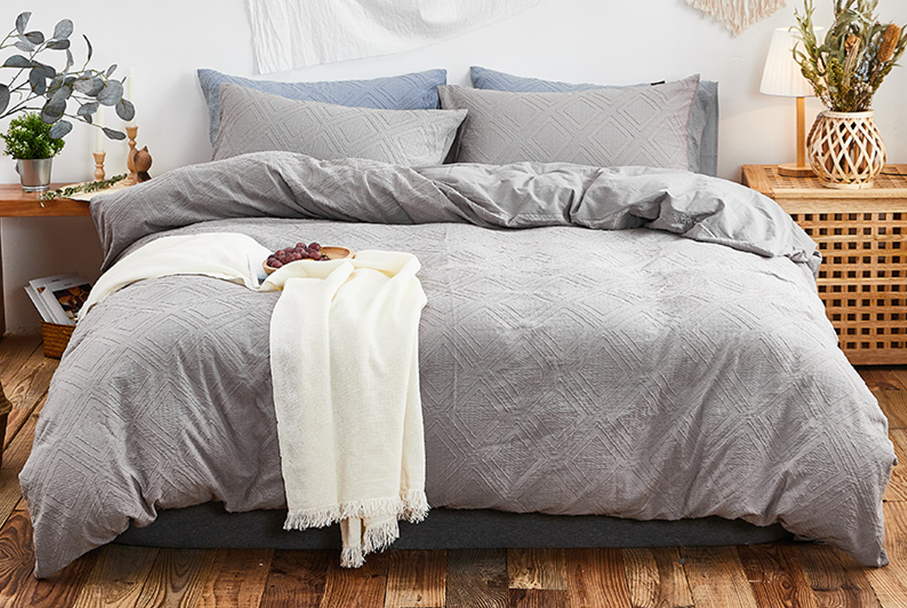


Cotton can be made into various specifications of fabrics. Cotton fabric is sturdy and wear-resistant, capable of washing and ironing at high temperatures. Cotton fabric absorbs moisture and removes moisture quickly
Fast and comfortable to wear.
The main and by-products of cotton have high utilization value, as previous scholars have said, "Cotton is a treasure all over. It is both the most important
Fiber crops are important oil crops, high protein grain crops, textile and fine chemical raw materials, and important strategic materials. Therefore, efforts must be made to increase cotton production, improve comprehensive utilization, increase production and appreciation, in order to increase cotton farmers' income and meet the needs of various aspects of national economic development.
Another unique use is for skincare and anti wrinkle beauty products.
Cotton is also an important honey source plant:
Cotton is divided into three types of nectaries: leaf veins, bracts, and floral nectaries, often secreted by the leaf veins before flowering. The flowering period of cotton in the provinces of the middle and lower reaches of the Yangtze River is from late July to early September, in the provinces of the middle and lower reaches of the Yellow River from early July to early August, and in Turpan, Xinjiang from mid July to early September. The honey flow period is about 40 days, and the optimal temperature for honey secretion is 35 ℃. The cotton production in Xinjiang generally ranges from 10 to 30kg, with a maximum of 150kg. Due to the frequent application of pesticides during the flowering period in other cotton areas, excessive damage to bees has greatly reduced the value of honey source utilization, with a group yield generally ranging from 10-20kg. Since the 1980s, the cotton area in China has grown rapidly, and some provinces and regions have actively promoted biological control technologies. It has become the main source of honey in the local summer and autumn.
Major cotton producing regions in the world
China, the United States, India, Uzbekistan, Egypt, etc. Among them, China has the largest unit production, and Uzbekistan is known as the "country of platinum".





 +86 15006286210(WhatsApp)
+86 15006286210(WhatsApp) +86-513-86102609
+86-513-86102609 Group 4,Lu Fu Qiao Village,Xing Dong
Street,Tong Zhou District, Nan Tong City
Group 4,Lu Fu Qiao Village,Xing Dong
Street,Tong Zhou District, Nan Tong City